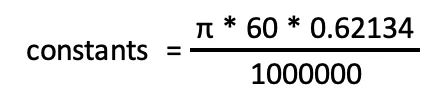This is typically presented as a specific number of watt hours (Wh). This means that the battery can deliver a certain number of watts per hour.
For example a 600Wh battery can deliver 600W for a single hour, or 300W for 2 hours, etc.
So how do we calculate the capacity - the Wh - of the battery?
What information do we need?
We require just two simple pieces of information:
- The Voltage Rating of the battery
- The Ah Rating of the battery
To calculate the battery capacity we use a simple calculation given by:

The Cyan Cycles e-bike battery calculator can be used to calculate the capacity for the Cyan Cycles product line.
Just select the Cyan Cycles e-bike from the drop-down list and the values for the voltage and the Ah rating of one battery will be automatically entered.
You can also select the units that will be used for displaying other calculated values in the results table
- Distance units
- Weight units
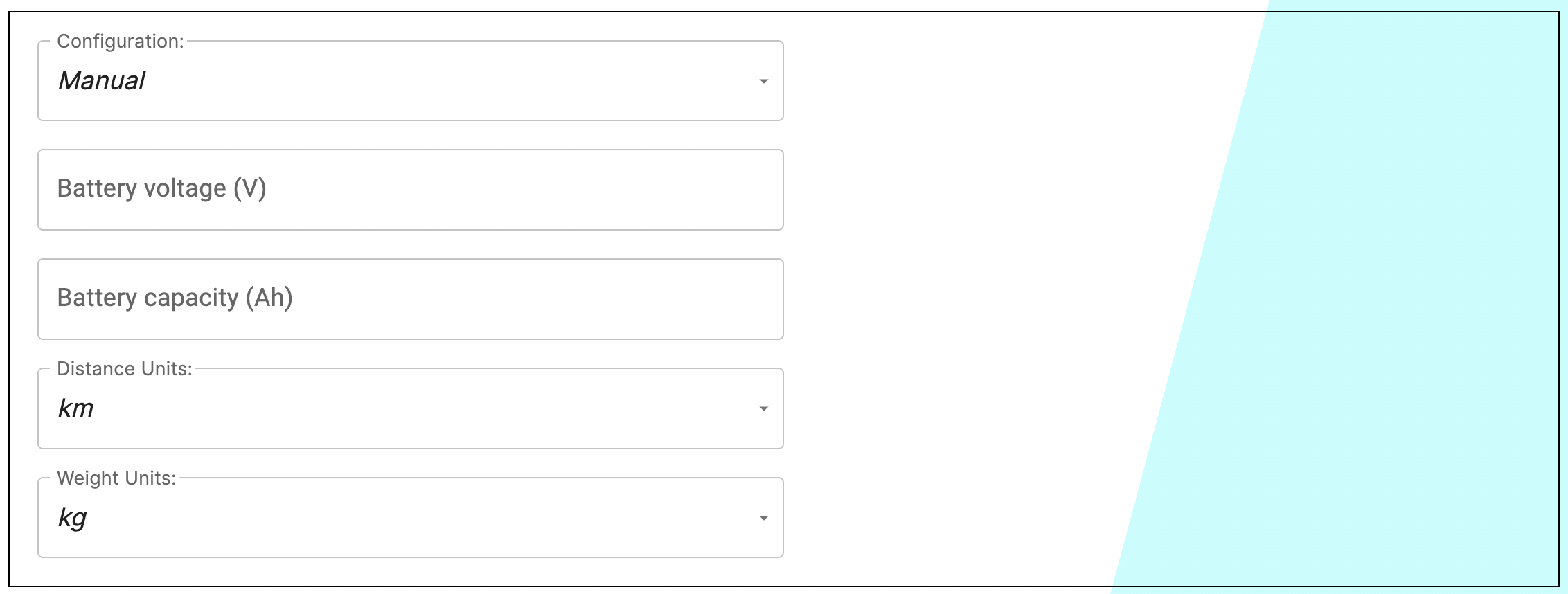
The results table below will then indicate three parameters related to your e-bike battery
- The battery capacity in Wh
- The autonomy (riding range of the e-bike)
- The weight of one battery

- Kilometres per Wh = 0.215 km/Wh
- Miles per Wh = 0.133 mi/Wh
- Wh per kg = 150 Wh/kg
High gear ratios are beneficial when riding at speed.
Low gear ratios provide a greater torque but move the wheel more slowly.
So how do we calculate the gear ratio.
What information do we need?
We require just two pieces of information:
- The Number of Teeth on the Chain Ring
- The Number of Teeth on the Rear Sprocket
To calculate the gear ratio we use the following formula:

To take into consideration the size of the wheel we can look at Metres of Development.
This is the distance the bike will travel for one revolution of the pedals.
We require one additional piece of information:
- The external diameter of the rear wheel (and tyre) in mm
To calculate the metres of development is then another simple calculation given by:

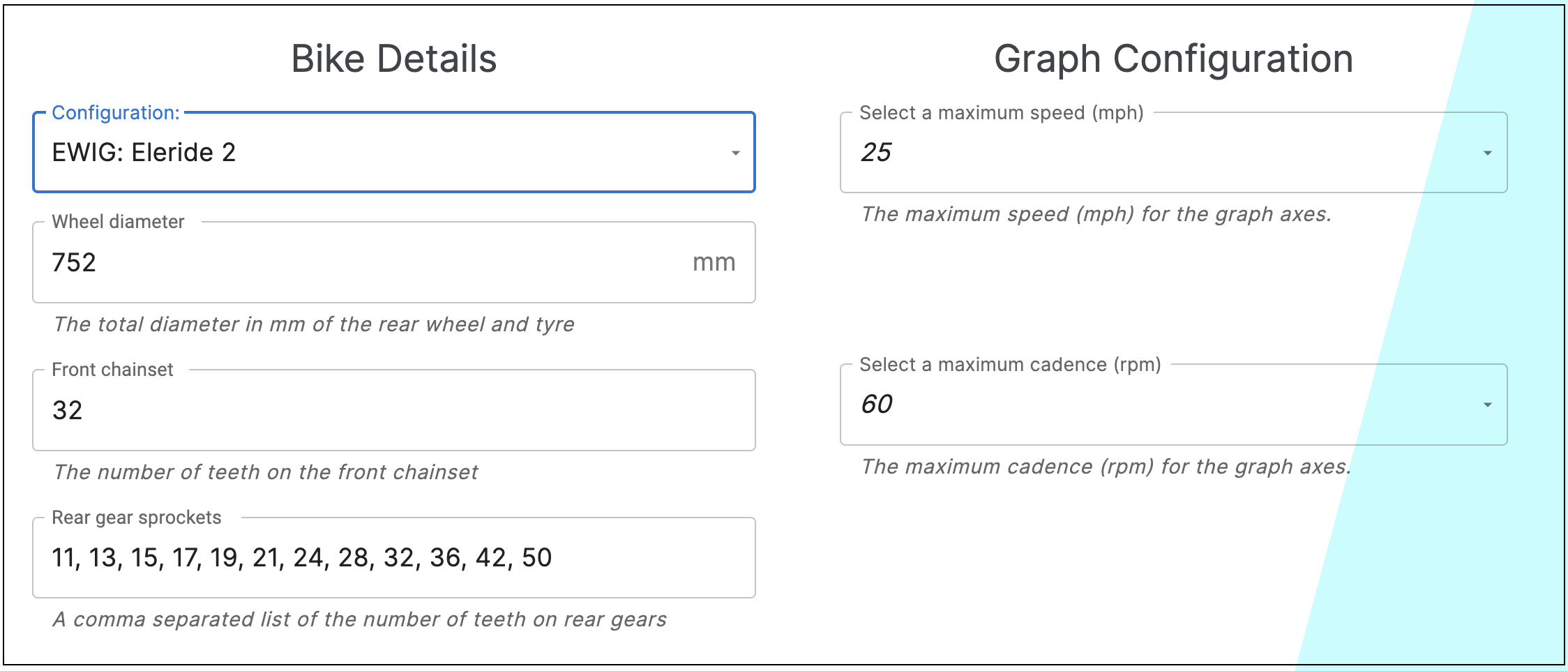
Just select the Cyan Cycles e-bike from the drop-down list and the values for the rear wheel size, the Number of Teeth on the Front Chain Ring and the Number of Teeth on each of the individual Rear Gear Sprockets will be automatically entered
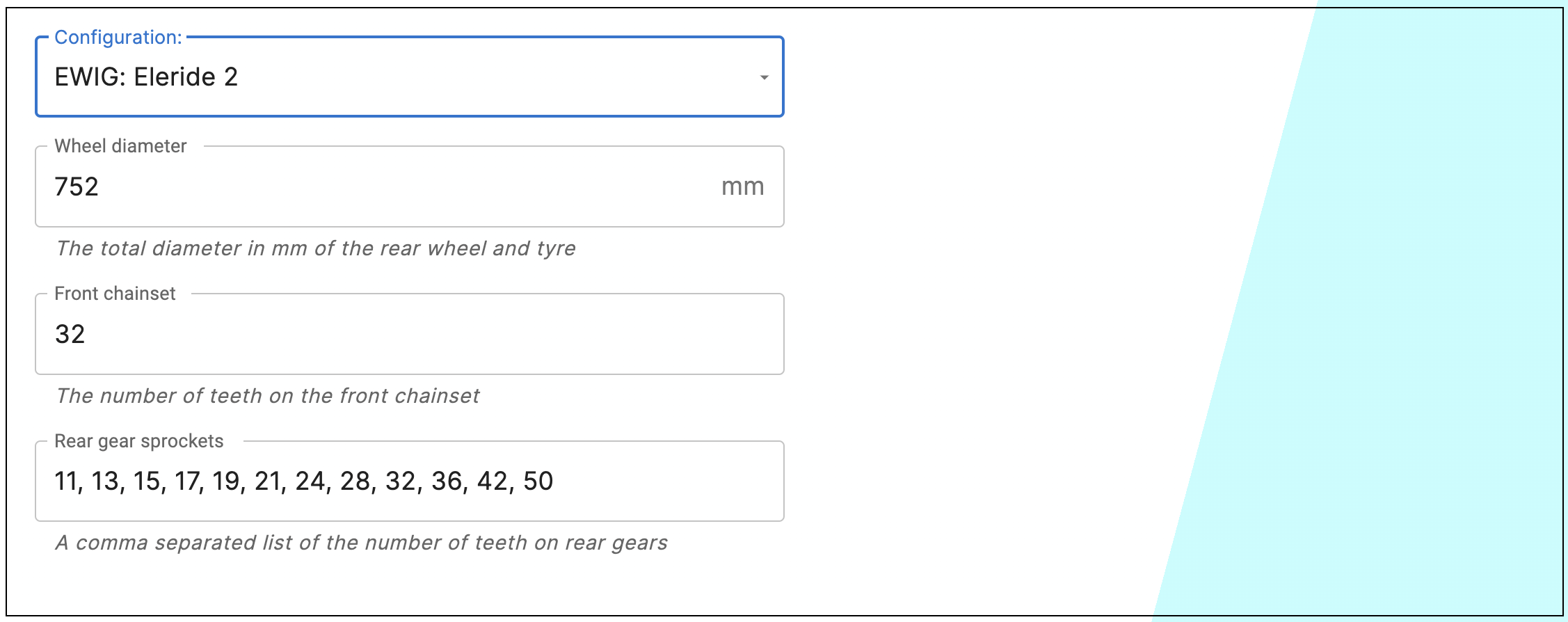


There is also the facility to select manual data entry, rather than one of the pre-set Cyan Cycles product line e-bikes
The data that should be entered, and the format, should be:
- The rear wheel diameter, including the tyre thickness, in mm
- The Number of Teeth on the Chain Ring
- The Number of Teeth on the Rear Sprocket, a comma separated list of the teeth on each cog
How can we calculate the range of an e-bike?
Some typical factors affecting the range of an e-bike are:
- Battery Charge Level
- Weight and Load Capacity
- Riding Style
- Tyres
- Terrain
- Assistance Level
- Pedalling
- Gear Shifting
- Weather
Each of these factors can have a significant effect on the range of an e-bike.
We need to make a few assumptions, based upon experience and the prevailing literature on the subject.
On average, it has been estimated that the average ebike battery will yield one mile of travel for every 20 Wh of energy.
So if your average speed will be 20 miles per hour you will be using approximately 20 Wh of energy. The more you pedal the less the Wh the e-bike has to provide to maintain that speed.
If we are looking at kilometres then this figure has been estimated to be one kilometre of travel for every 12.3 Wh of energy.
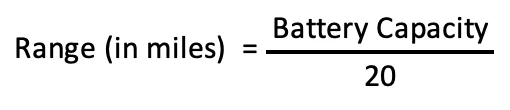
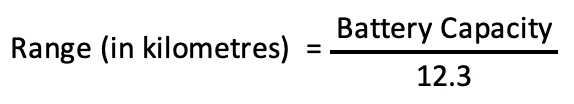
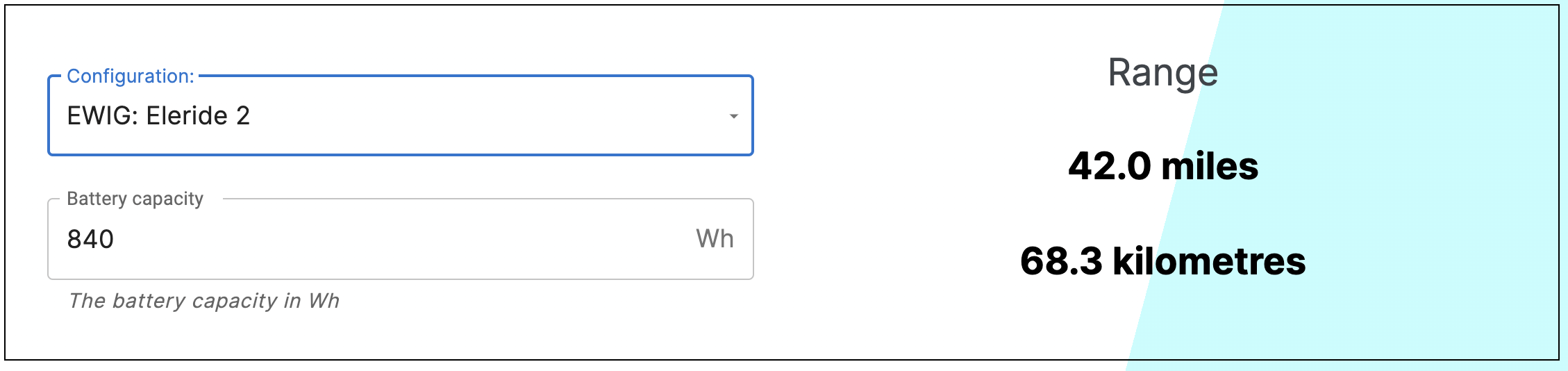
You can select the pre-set Cyan Cycles e-bike from the dropdown list in the data entry section, and the results will appear as shown below
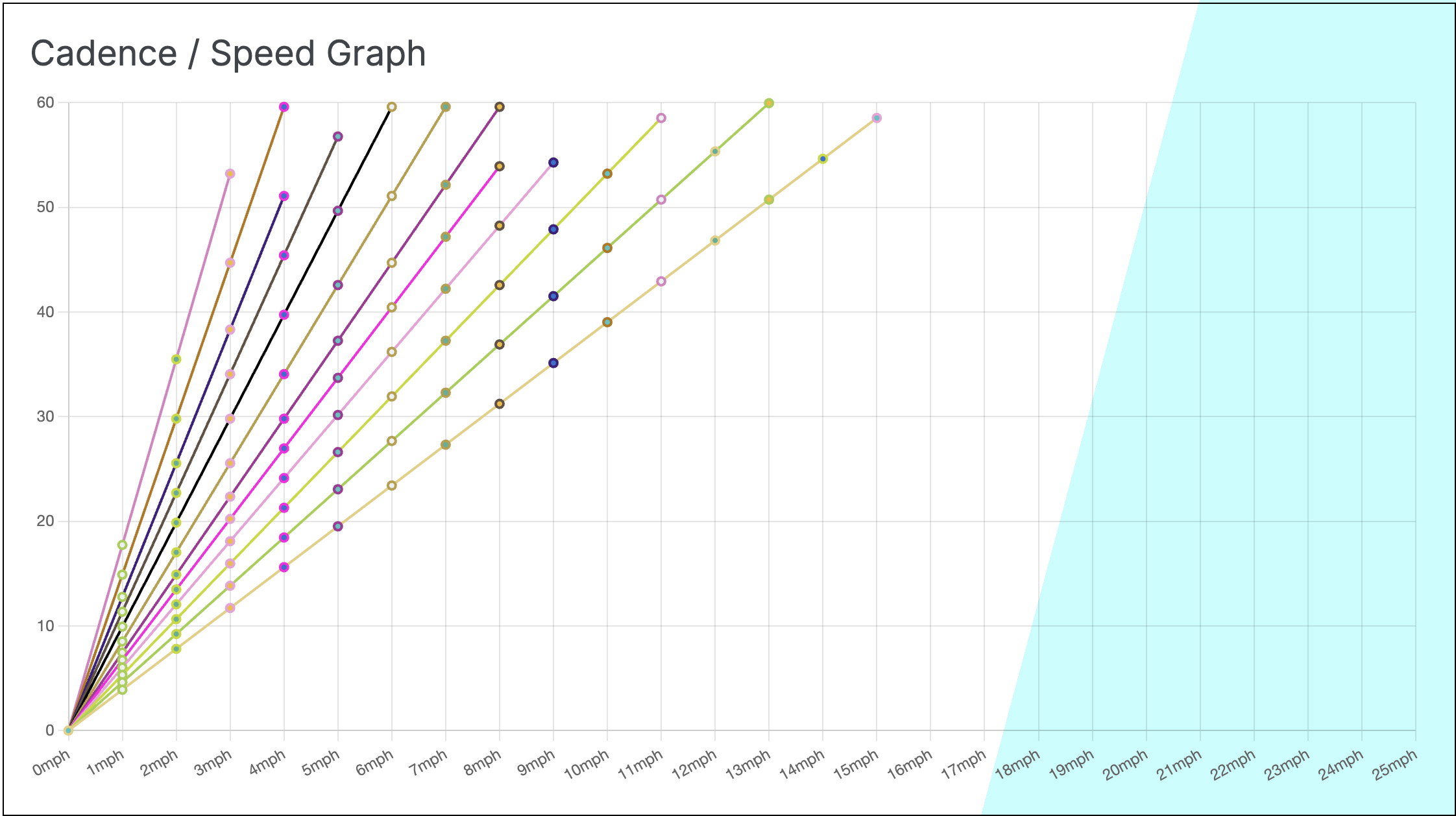
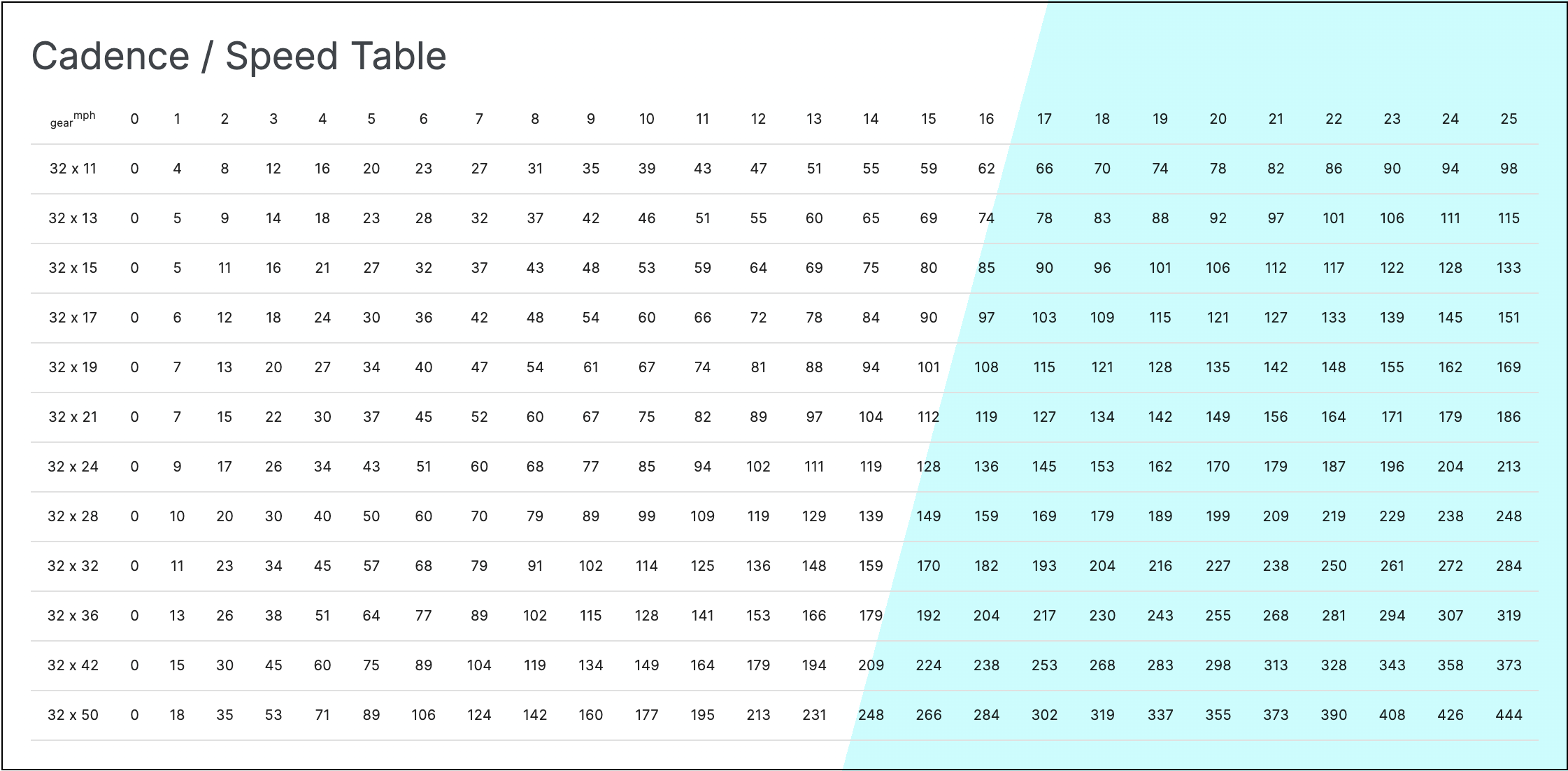
The cadence is the number of revolutions of the pedals per minute (rpm).
We can calculate the cadence required to meet certain speed expectations, without taking into account any power assist.
If we are utilizing the power provided by an e-bike we can maintain higher speeds and increase the range of an e-bike.
There are a number of factors that can affect the ability to maintain a particular cadence, including:
- Wind Speed
- Terrain
- Surface
- Gear Ratio
Select the Cyan Cycles e-bike from the list in the data entry section and choose the desired graph and table values to be presented.
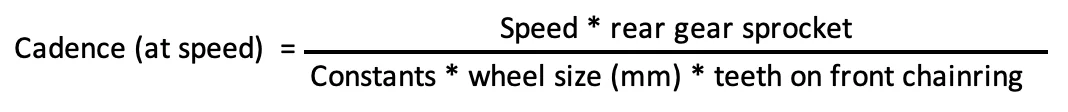
These constants can be combined into the following calculation.